Weed intrusion and soil instability make creating a durable gravel driveway or a perfect landscape pretty troublesome. Besides, one of the solutions that can be used is geotextile fabric which is a simple but very effective solution to these problems. Geotextiles fabric’s ability to provide stability, weed prevention and super drainage has turned it into a revolution not just for the homeowners but also the landscapers. The article will uncover the advantages of geotextile fabrics for driveways and landscapes and also provide practical tips on how it can turn your outdoor areas into long-lasting, functional, and stunning zones. Go ahead and read to find out how this multifunctional material can equal less time, effort, and money spent while still delivering professional results.
Geotextile Fabric Explained
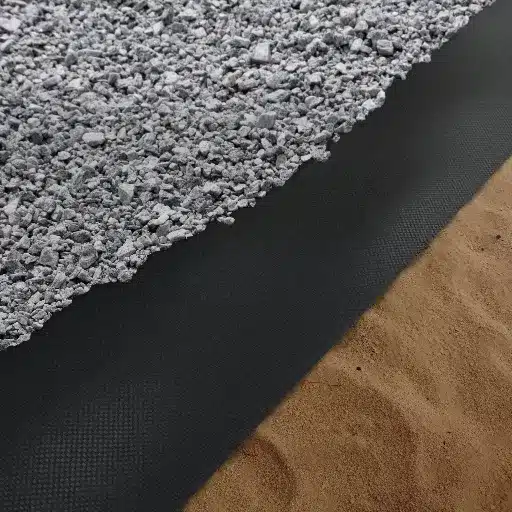

Geotextile fabric is a breathable substance that has numerous uses in landscaping and construction, such as giving support, draining, and preventing soil erosion. At the same time, it serves as a barrier but allows water to flow, which makes it a perfect choice for the construction of driveways and landscaping projects.
Definition and Key Purposes
Geotextile fabric is a permeable product that is produced with synthetic fibers such as polyester or polypropylene, for the purpose of being employed in construction and landscaping projects to do several functions. It is made to be strong, resistant to weather changes, and to have so many properties that it can be used in various environmental and structural issues. The fabric’s basic functions are as follows:
Separation: In fact, Geotextile fabric will not let different layers of soil and aggregate intermingle, thus ensuring that your project would be stable and perform well. For example, if you have a driveway, it will not let the subsoil seep into the base material, thus retaining the strength of the driveway over time.
Filtration: Geotextile fabric, while that it permits water to go through, will stop the movement of even fine soil particles. This feature is very important in drainage setups because the most common reason for drainage failure is the soil getting clogged.
Reinforcement: The use of geotextile fabric simply means reinforcing the weak soil with structural support thus, increasing its load-bearing capacity. If so, geotextile can be very handy in retaining walls, roads, or any surface that will bear heavy loads.
Drainage: The use of geotextile fabric helps to drain out the water naturally, since it allows water to flow while reducing soil compaction, hence, no more water pooling or erosion in the landscape.
Erosion Control: The fabric acts as a barrier, reducing soil displacement caused by wind, rain, or flowing water. This is especially important for slopes and shores.
Geotextile Fabrics Varieties
Geotextile fabrics are typically classified into three major types according to their manufacturing processes and characteristics—woven, non-woven, and knitted geotextiles. Every type is designed for different uses, which makes geotextiles highly flexible in contemporary construction and engineering works.
Woven Geotextiles
The production of woven geotextiles is done by interweaving synthetic threads and the outcome is a fabric with remarkable strength and durability. Among the various applications, soil stabilization, erosion control, and retaining wall reinforcement are the most common. Woven fabrics, in general, have lower permeability but have a higher resistance to loads, thus making them ideal for road construction projects and heavy-duty applications. For instance, scientific investigations claim that the introduction of woven geotextiles in pavement systems may enhance the load-bearing performance by nearly 30%.
Non-Woven Geotextiles
On the other hand, the production of non-woven geotextile fabrics employs several methods including, for instance, needle-punching and heat bonding that result in very permeable fabric. Non-woven geotextile materials are perfect for filtration and drainage because they permit water to go through without allowing soil particles to clog the drainage system. Some of the most common uses include under drains, separation layers, and landfills where geomembranes are protected. The research indicates that non-woven geotextiles can increase the drainage systems’ life span by up to 40%, thus lowering the maintenance cost in the long run.
Knitted Geotextiles
Knitted geotextiles are the least popular types but they are made by linking a series of loops of yarns together. These fabrics are both flexible and strong, consequently, they are often used in specialized applications that require designing and adapting to features. For example, knitted geotextiles are very good at supporting the steep slopes and the ones with difficult topography.
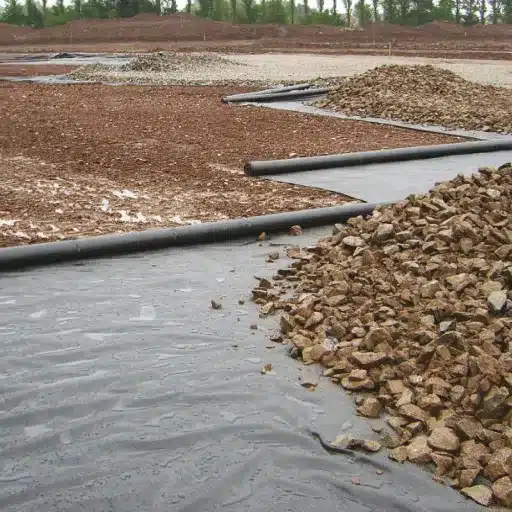
Geotextile Fabric Under Gravel – The Benefits
When gravel is applied with the geotextile fabric, the performance of the gravel will be better because of improved drainage, no erosion, and more stability. Besides, there will be no soil under the gravel to mix with the gravel and a longer-lasting gravel surface will be the result. Besides, it leads to a decrease in the maintenance required and can be more economical for the whole structure in the long run.
Soil Stabilization and Support
The use of geotextiles in soil stabilization and support is essential. In this case, the fabrics separate the soil from the aggregate materials and, consequently, mixing takes place and the ground’s structural integrity is maintained. It is especially important for roads, railways, and foundations, where uneven settling of soil can cause to the structure being damaged long term. Studies indicate that geotextiles could enhance soil bearing capacity by 50% which is very economical solution to load-bearing surfaces enhancement. Moreover, they serve as a barrier against erosion since they keep soil particles in place even if they are located within run-off or heavy rainfall areas.
Geotextiles have already proved their effectiveness in many different areas. For example, in the case of unpaved roads; using it in construction gives an impression that the lifespan of graveled roads is extended, which is done by lessening rutting and hence gravel loss. The saving from the process can amount up to 30% in a year’s time with fibers like woven, non-woven, or knitted type being applied for such applications. In accordance with the enablingpromise of these materials, geotechnical engineers can successfully tailor their specific projects’ needs and, thus, the performance in diverse environmental challenges is sure to be optimal.
Weed Control and Filtration
Geotextile fabrics are probably one of the best ways for weed control and filtration in landscaping and agriculture and are thus, not only very useful for soil stabilization. These fabrics act as a barrier layer and effectively filter water and nutrients through to the plants while preventing weeds from coming into the cultivated soil areas. The double task is being achieved through the use of permeable geotextiles that have a proper filtration and separation system.
Recent studies have also proved that the application of geotextile weed barriers can lessen invasive weeds by as much as 90%, thus, a major reduction of chemical herbicides is required. This method of controlling weeds is both environmentally safe and financially viable in the long run. In addition, geotextiles have not only replaced plastic mulch, but they are also considered better alternatives since, unlike plastic, geotextile fabrics do not contribute to soil contamination with microplastics. The use of geotextiles is now very common in drainage systems, where they act as soil particle traps so that the waters from the pipes and ditches could run freely without the need of constant maintenance. These new developments are making geotextile fabrics important in the modern environmental and agricultural management systems.
Applications of Geotextile Fabric in Construction and Landscaping

There are a number of reasons why geotextile fabric should be used in construction and landscaping. It is important to soil stabilization, erosion control, and even better drainage. Moreover, it works as a great barrier for the prevention of weeds in landscaping, thus being a practical and environment-friendly alternative in the different applications.
Enhancing Drainage in Gravel Driveways
The application of the geotextile fabric to gravel driveway construction has a lot to do with its durability and technical drainage performance being assured for a long time. In the first place, gravel driveways, beside being economically attractive and aesthetically nice, are subject to all the drawbacks of the usual soil erosion, ruts, and poor drainage. Geotextiles take a place between the subsoil and the gravel giving no chance for mixing yet letting water go through the driveway.
An advantage of the geotextile fabric application that could be singled out as the strongest is the increase in the driveway’s load-bearing capability. As per the latest studies, the addition of geotextiles can lead to as much as 30% displacement of the gravel reduced which means a significant decline in the requirements for frequent maintenance and new gravel. Besides, the statistics reveal that the driveways featuring geotextile layers undergo up to 50% reduction in surface water pooling as compared to those without such layers.
Landscaping Projects and Erosion Control
Applying geotextile fabric not only for the construction of gravel driveways but also for landscaping projects and erosion control is crucial. The fabrics are made with the sole purpose of stabilizing earth, controlling water, and being up to erosion in places of irregular ground or age-old affected by weather. The figures of recent times show that the application of geotextiles as part of drawing up a proper erosion control plan can lead to a reduction of soil loss by up to 90%, thus making them a great choice for high-quality landscaping for both residential and commercial sectors.
Separation of soil layers, improvement of drainage, and allowing plants to be able to take their roots are the main mechanisms by which geotextiles combine the soil naturally over the course of time. As an illustration, in retaining wall constructions or slope stabilization sites, non-woven geotextiles are in charge of drainage and pressure reduction which prolongs the life of the building. Besides, woven geotextiles are exceptionally tough and thus are employed in high-stress applications like the retention of steep slopes or the fortification of paths in leisure parks.
Selecting the Right Geotextile Fabric

The right geotextile fabric will be chosen depending on the specific purpose and the characteristics needed. I will use non-woven geotextiles for their high permeability in drainage and filtration. In the case of reinforcement or load distribution, woven geotextiles are the ones I will go for because of their strength and longevity.
Choosing Between Woven and Non-Woven Fabrics
The differences between woven and non-woven materials have to be known when selecting geotextile fabrics. This knowledge is crucial for the performance of the fabrics in the specific applications. Woven geotextiles are produced by intertwining synthetic fibers to form a durable, grid-like structure. These fabrics are well-adapted to very high-strength projects like soil stabilization and heavy load-bearing applications, e.g., building of gravel roads or parking lots. Their tensile strength allows them to very effectively prevent soil erosion and provide lasting support in areas with high stress. Research has shown that woven geotextiles can handle tensile strengths in the range of 200 to 500 pounds per inch, depending on the material used.
In contrast, non-woven geotextiles are made through a bonding process that usually involves heat or needles and that sulks synthetic fibers to form a material that looks and feels like felt. They are more adaptable and primarily used in filtration, drainage, and horticulture works. Non-woven fabrics are very good at letting water pass through, which helps control moisture and keeping waterlogging at bay. For instance, non-woven geotextiles can attain a permeability rate of up to 0.2 gallons per square foot per second, thus making them highly suitable for drainage trenches or erosion control in marshy areas.
Heavy-Duty Options for High-Traffic Areas
Extremely durable and able to bear constant stressing and pressuring are the qualities that geotextile fabrics should possess when used in high-traffic places like highways, parking lots, or industrial yards. Heavy-duty woven geotextiles are generally the best choice for such applications due to their high tensile strength and even load distribution over the substrate. For example, polypropylene woven geotextiles have a tensile strength of up to 200 kN/m which not only makes them an excellent choice for avoiding rutting and base layer deformation in heavily trafficked areas but also contributes to longevity of the pavement.
Moreover, combining geogrids with geotextile can further increase the load capacity by better stabilizing the aggregate layer. Studies have shown that combining geotextile stabilizers with gravel or crushed stone layers can extend the life of the road by 50%, thus resulting in less maintenance and increased cost efficiency in the long run.
Best Practices in Installation of Geotextile Fabric

For my installation of geotextile fabric, the first thing I do is to clear up the area, getting rid of any kind of rubbish or debris, and leveling the ground. Next, I take out the fabric and spread it out very carefully, looking for folds and wrinkles, and then cover the edges with at least twelve inches so that it will not be exposed.
Gravel Layering Techniques
Practicing the correct layering methods while laying the geotextile fabric under gravel is one of the prerequisites for making the most of the strength and stability of the whole structure. Here are some steps which, if followed, will give you the best results:
Ground Work
The first step is to clear the area from any rubbish, plants, and the top layer of soil, so as to get a firm and stable base. Remove all the uneven parts of the soil to create a nice flat surface for the geotextile fabric. According to the industry standards, the subgrade should be compacted to form a solid base with a compaction rate of at least 95% of the modified Proctor density.
Geotextile Fabric Installation
Lay out the geotextile fabric on the prepared subgrade, making sure that it is perfectly flat with no wrinkles or creases. The fabric should be beyond the edges of the gravel by 6–12 inches so that there will be no migration and erosion at the edges during the use of the gravel. For the overlapping sections use at least 12–18 inches overlap, depending on the traffic in the area and the soil conditions.
Edge Anchoring
For the purposes of holding the geotextile in place and preventing its movement, appropriate anchoring devices like pins or stakes should be used at a distance of about 3–5 feet apart. This way, the fabric will not move during the process of adding and compacting the gravel.
Gravel Layers Distribution
The moment the geotextile is in place, let the gravel layer be applied uniformly on top of it. The gravel thickness for driveways or walkways is generally 4–6 inches for light traffic and up to 12 inches for heavy or commercial traffic. At first, put down a base layer of big angular gravel (like crushed stone of 1–2” size) to assist drainage and stability. Then, layered up with a finer one (for instance, crushed stone of 3/8” size) to have a even surface.
Longevity and Effectiveness Maintenance Tips
For the geotextile installation beneath gravel to be long-lasting, effective, and durable, regular maintenance practices are to be followed. The first step of maintenance involves the inspection of the gravel surface so that any signs of wear, displacement, or uneven patches can be detected. If these problems are tackled quickly, then it is possible to save money on repairs, and the risk of further damage will also be lowered.
A really important point is to handle the drainage on the surface propertly. In the long run, water that has nowhere to go can cause the gravel on the top to erode and the geotextile underneath to lose its effectiveness. Therefore, seeing to it that the drainage systems are working properly and are not clogged will, in fact, keep the structural soundness of the gravel and the geotextile layers. The latest findings show that drainage systems that are kept in good condition can cut down surface erosion by as much as 30% which automatically means a longer life of the installation.
Reference Sources
-
Pro Fabric Supply Blog
- Article: 7 Reasons Why Professionals Always Use Landscape Fabric Under Gravel
- This source explains the benefits of using geotextile fabric, such as weed prevention and soil stabilization, making it a go-to material for professionals.
-
Mulch Pros Blog
- Article: Should I Use Landscape Fabric Under Gravel
- This blog discusses the advantages of geotextile fabric, including reduced weed growth, erosion control, and long-term cost savings.
-
Vodaland USA Blog
- Article: How to Use Geotextile Fabrics Under Gravel
- This source provides a detailed guide on the application of geotextile fabric, emphasizing its role in weed suppression and soil stabilization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does driveway fabric assist drainage?
Driveway fabric has a permeable characteristic that permits water to move through but hinders the germination of weeds at the same time. As water is being filtered, it is slowly released to prevent accumulation, which in turn could cause the formation of potholes or the washing away of soil.
What should be the gravel layer thickness when landscape fabric is used?
In general, the gravel layer thickness should be around 3 to 4 inches at the minimum when landscape fabric is used. Such thickness guarantees the required drainage and firmness, particularly in heavy rains, plus it helps in not allowing the fabric to get punctured by the weight of the gravel.
What are the advantages withsolid ground of using a stabilization fabric under gravel?
The application of a stabilization fabric under gravel increases the distribution of loads, acts poreless to the gravel sinking into the soil, and gives a separation layer that limits weed growth. It produces a very strong support that also extends the lifetime of the surface.
How do I prepare the area and put down the fabric for gravel installation?
Fabric for gravel installation should first be placed in the area from which all debris and vegetation have been removed. Next, the fabric is rolled out over the prepared soil with necessary edges overlapping and then secured with landscape staples before the gravel is dumped on it.
What kinds of gravel are suitable to be used with geotextile fabric?
With geotextile fabric, it is possible to use different types of gravel, such as crushed rock, aggregate rock, and rock gravel. When these materials are laid over the fabric in the right way, they will offer excellent drainage and stability.







